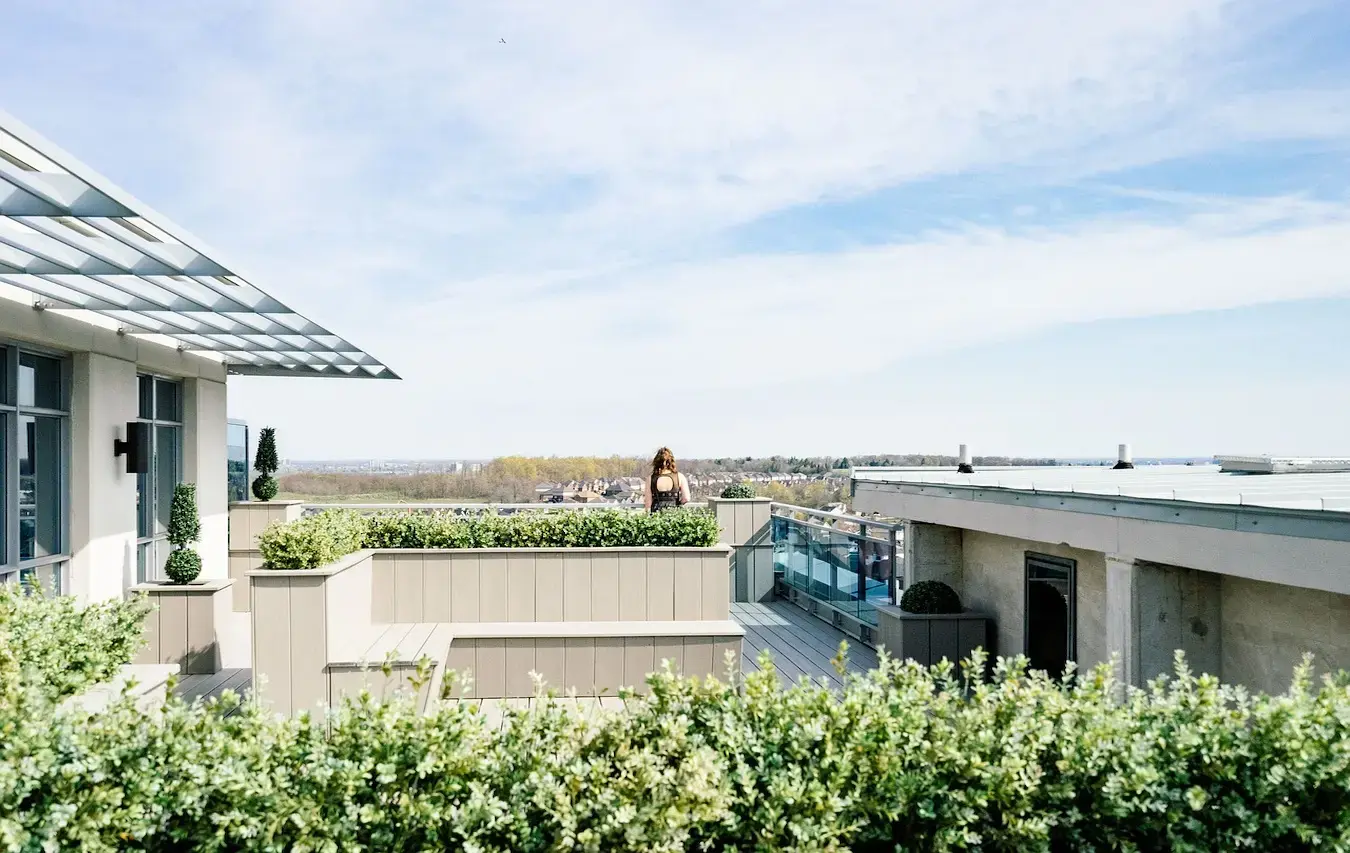
Introducing Curvspace Rooftops
Curvspace Rooftops offer a unique blend of modern design and functional versatility, inspiring you to transform these separating spaces into more functional, beautiful, and enjoyable places for everyone. With a focus on sustainability, these rooftops incorporate eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient systems, maximizing natural light and integrating green spaces to create harmony with urban surroundings. Key design elements include structures for visual appeal, wind resistance, and rainwater drainage, along with reflective surfaces to reduce cooling needs. Sustainability features include recycled materials, solar panels, and rainwater harvesting systems. Versatile in function, Curvspace Rooftops serve as communal spaces, event venues, and private retreats, enhancing urban living by providing recreational areas, increasing property value, and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Reader Disclosure
Jump to:
What is a rooftop?
A rooftop is the uppermost surface or structure of a building, providing a unique vantage point. Rooftops can vary greatly in design, function, and materials used. Examples include flat roofs, pitched roofs, and curved roofs. Not only do rooftops offer protection from elements, they also present opportunities for creative uses.
In urban settings, rooftops often transform into gardens, terraces, or social hubs. Rooftop gardens utilize space for greenery and contribute to environmental sustainability. Terraces offer open areas for relaxation or entertainment, enhancing urban living with recreational spaces.
Modern rooftops integrate advanced design and sustainability features. These rooftops use eco-friendly materials, solar panels, and rainwater harvesting systems. The innovative designs include structures and reflective surfaces, improving both aesthetics and energy efficiency.
Rooftops serve various purposes beyond just shelter. They act as communal spaces, event venues, or private retreats. By converting rooftops into multifunctional areas, urban environments gain valuable recreational and social amenities. This not only enhances property value but also promotes healthier lifestyles and community well-being.
The History of Rooftops
Rooftops have been integral to architecture for thousands of years. Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamians and Egyptians utilized flat rooftops for communal activities and storage spaces. These early rooftops were often constructed from materials like mud bricks and reeds.
During the Roman Empire, rooftops evolved into more sophisticated structures with the introduction of sloped and gabled designs. Romans used tiles and other durable materials, improving both aesthetics and durability. Rooftop gardens and terraces became popular among the affluent, serving as private retreats and social areas.
In the medieval period, European rooftops featured steep slopes and intricate detailing. These designs helped manage snowfall and provided added protection from the elements. Castles and fortresses had functional rooftops for defense, including lookout points and battlements.
The Industrial Revolution introduced new roofing materials, such as metal and concrete. Advances in technology allowed for more complex and durable rooftop designs. Urbanization led to the development of rooftop gardens and terraces, reclaiming green spaces in crowded cities.
Today, modern rooftops incorporate advanced materials and technologies. Sustainable and energy-efficient designs are prioritized, with features like solar panels, green roofs, and rainwater harvesting systems. Urban rooftops serve as social hubs, recreational areas, and eco-friendly solutions for contemporary living.
Purpose of Rooftops
Rooftops serve multiple purposes, making them essential components in architecture and urban planning. Providing shelter from weather elements like rain, snow, and sunlight is the primary function of a rooftop. Historical structures utilize rooftops to enhance durability and ensure inhabitants’ comfort.
Rooftops play a significant role in energy efficiency. For example, incorporating solar panels on rooftops generates renewable energy, reduces electricity costs, and lowers carbon footprints. Green roofs offer insulation, regulate indoor temperatures, and promote biodiversity.
Rooftops also serve as valuable spaces for social and recreational activities. Modern urban environments utilize rooftops for gardens, restaurants, and recreational areas. These spaces offer residents and visitors a peaceful retreat from the bustling city below.
Sustainability is a critical aspect of contemporary rooftops. Integrating features like rainwater harvesting systems and reflective materials helps conserve resources and mitigate urban heat island effects. By adapting these sustainable practices, rooftops contribute to creating eco-friendly urban ecosystems.
Types of Rooftops
Flat Roofs
Flat roofs offer simplicity in design and ease of access for maintenance tasks. Typically constructed with asphalt, gravel, or rubber, these roofs are common in commercial buildings and urban residential spaces. Though flat, they usually have a slight slope for water drainage.
Gable Roofs
Gable roofs feature two sloping sides that form a ridge at the top. This design facilitates water runoff and provides ample ventilation. Often seen in residential homes, gable roofs can withstand various weather conditions, making them popular in areas with heavy rainfall.
Hip Roofs
Hip roofs have four sloping sides, providing stability and strength. This type of roof is ideal for regions prone to high winds and hurricanes. The equal slopes enhance durability, reducing the risk of damage during severe weather.
Mansard Roofs
Mansard roofs, known for their French architectural influence, have four sides with two different slopes. The lower slope is steeper than the upper one, offering additional living or storage space within the attic. These roofs are common in historic and upscale residential buildings.
Skillion Roofs
Skillion roofs, also called shed roofs, consist of a single sloping surface. They are easy to construct and provide a modern aesthetic. These roofs are often used for extensions or smaller structures like garages and sheds.
Green Roofs
Green roofs incorporate vegetation and soil layers. They enhance energy efficiency, manage stormwater, and improve air quality. Suitable for both residential and commercial properties, green roofs offer eco-friendly benefits and aesthetic appeal.
Solar Roofs
Solar roofs integrate photovoltaic panels, converting sunlight into electricity. They contribute to energy savings and reduce reliance on conventional power sources. Ideal for environmentally conscious homeowners, solar roofs also add property value.
Dormer Roofs
Dormer roofs feature a windowed structure that projects vertically from a sloping roof. This design increases usable space and allows natural light to enter the attic or upper floors. Dormer roofs are prevalent in older homes and blend well with different architectural styles.
Butterfly Roofs
Butterfly roofs consist of two inward-sloping surfaces that form a V-shape. They facilitate the collection of rainwater and provide a distinctive, modern look. Often found in contemporary homes, butterfly roofs offer both functional and aesthetic advantages.
Each type of rooftop offers unique benefits tailored to specific needs, climates, and architectural styles.
Contemporary Uses of Rooftops
Rooftops today serve a range of innovative purposes, enhancing urban living spaces and sustainability. Many rooftops now function as urban farms, growing fresh produce and reducing the food transportation carbon footprint. These farms, like Brooklyn Grange in New York City, transform otherwise unused vertical spaces into productive agricultural zones.
Another popular use of rooftops is as social hubs. Rooftop bars and restaurants offer vibrant settings with expansive city views, making them sought-after destinations. Cities like Bangkok and New York City are known for their rooftop venues that blend entertainment with stunning panoramas.
Green roofs are another contemporary trend, promoting energy efficiency and biodiversity. By covering rooftops with vegetation, these installations reduce heat absorption, lower energy costs, and provide natural habitats for wildlife. Chicago’s City Hall is a notable example that showcases sustainable design influencing urban planning.
Solar panel installations have become integral to many modern rooftops, enabling buildings to generate renewable energy. Businesses and homeowners alike adopt this technology to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and cut energy expenses. Countries like Germany have heavily invested in solar energy, demonstrating its viability on a large scale.
Rooftops also double as recreational spaces. In dense urban areas, rooftops offer residents areas for relaxation and leisure, often featuring swimming pools, gardens, and playgrounds. Rooftop cinemas can be found in cities like Melbourne, offering unique outdoor movie experiences.
Lastly, rooftop co-working spaces address the need for flexible working environments. These open-air offices provide natural light, fresh air, and inspiring views, catering to professionals seeking productivity outside conventional office settings.
These contemporary uses of rooftops not only maximize space but also contribute significantly to creating sustainable, vibrant urban environments.

Modern Trends in Rooftop Design
Modern rooftops prioritize sustainability and social interaction. Green roofs reduce urban heat and enhance biodiversity by incorporating plants and natural elements. Rooftop gardens promote local food production, cutting carbon footprints and enhancing air quality.
Solar panels dominate the energy efficiency trend. These installations harness renewable energy, decreasing reliance on non-renewable sources and lowering utility costs. Innovations in lightweight and flexible panels allow for diverse applications.
Community-centric designs turn rooftops into social hubs. Rooftop bars offer breathtaking city views and vibrant atmospheres. Rooftop restaurants provide unique dining experiences, blending ambiance with culinary excellence.
Rooftop recreational spaces cater to diverse interests. Swimming pools offer leisure and luxury. Rooftop cinemas provide immersive movie-watching experiences, combining entertainment with stunning skylines.
Rooftop co-working spaces optimize urban density and adapt to modern work trends. These flexible work environments encourage productivity and collaboration with inspiring city views.
Eco-friendly materials drive contemporary rooftop designs. Recycled and sustainable materials reduce environmental impact, aligning with global ecological goals.
Maintaining this multifunctional approach, modern rooftop designs contribute significantly to urban sustainability and vibrant city life.
Cultural Diversity in Rooftop Design
Rooftop designs around the world reflect a rich diversity of cultural influences. Asian rooftops, for example, often feature tiles inspired by traditional pagodas, promoting harmony with nature. Japanese roof gardens incorporate Zen elements, creating tranquil retreats.
European cities showcase distinct rooftop styles. Parisian rooftops, characterized by mansard roofs, offer aesthetic symmetry and practical attic space. In contrast, Mediterranean regions utilize terracotta tiles and whitewashed surfaces to reflect sunlight and cool interiors.
Middle Eastern rooftops adapt to arid climates. Flat roofs double as living spaces, with shaded areas for communal gatherings. Intricate mosaics and geometric patterns add an artistic touch to these rooftops.
Latin America embraces colorful rooftop designs. Mexican rooftops use vibrant tiles and murals, turning rooftops into artistic canvases. Brazil’s favelas convert rooftops into social hubs, fostering community interaction and resourcefulness.
Modern urban rooftops integrate cultural elements with functional design. In New York City, rooftop gardens and lounges echo the city’s eclectic character, blending greenery with skyline views. Singapore’s Marina Bay Sands exemplifies innovative design, featuring a rooftop infinity pool that merges luxury with architectural prowess.
Diverse cultural influences enrich contemporary rooftop designs, providing practical and aesthetic benefits. Each culture adds unique elements to the urban landscape, enhancing the multifunctional role of rooftops in today’s cities.
Curvspace Qualities of Rooftops
Modern rooftops exhibit unique Curvspace qualities, enhancing their aesthetic and functional aspects. With advancements in architectural design, rooftops now feature fluid lines and organic shapes to maximize space and functionality.
Fluid Lines and Organic Shapes
Architects integrate fluid lines and organic shapes into rooftop designs to optimize space. Surfaces provide better wind resistance and water drainage, improving structural integrity. These shapes also offer more versatile area usage, accommodating amenities like rooftop pools and gardens.
Improved Aesthetic Appeal
Rooftops enhance visual appeal. Unique designs attract attention and set buildings apart from traditional structures. For instance, wave-like forms and dome-shaped coverings create striking silhouettes, contributing to urban skylines’ distinctiveness.
Multi-Functional Use
Rooftop spaces support multi-functional uses. Smooth, continuous surfaces provide flexible layouts for diverse activities. Green roofs, solar panel installations, and recreational areas benefit from these designs, making rooftops more adaptable to different urban needs.
Enhanced Environmental Performance
Curvspaces boost environmental performance. Roofing materials absorb less heat, reducing urban heat island effects. Efficient rainwater drainage systems integrated into designs lower flood risks, promoting sustainability in city environments.
Case Studies and Examples
Numerous examples showcase the effectiveness of curvspace qualities. Bjarke Ingels Group’s VM Houses in Copenhagen utilize wave-shaped rooftops to combine aesthetic value and community spaces. The Marina Bay Sands in Singapore features a green space at the top, blending luxury with practical environmental design.
Curvspace qualities inspire you to transform rooftops into versatile, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing urban elements.
People Also Ask
What are green roofs?
Green roofs are rooftops covered with vegetation. They help reduce urban heat, provide insulation, and improve air quality.
How do rooftop gardens contribute to urban environments?
Rooftop gardens enhance green space in cities, promote biodiversity, and offer community relaxation areas. They also improve air quality and reduce heat.
What are Curvspace qualities in rooftop designs?
Curvspace qualities include fluid lines and organic shapes that optimize space, improve wind resistance, and enhance water drainage on rooftops.
Why are solar panels commonly installed on rooftops?
Solar panels utilize rooftops to harness sunlight, providing renewable energy and reducing electricity costs in urban areas.
What is the role of community-centric designs in modern rooftops?
Community-centric designs create social spaces like rooftop bars and recreational areas to foster social interaction and community engagement.
How do eco-friendly materials improve rooftop sustainability?
Eco-friendly materials reduce the environmental impact of rooftops by enhancing energy efficiency, durability, and overall sustainability.
What are some notable examples of innovative rooftop designs?
Notable examples include Bjarke Ingels Group’s VM Houses and Marina Bay Sands in Singapore, showcasing versatile and aesthetically pleasing rooftop designs.
How do co-working spaces benefit from rooftop locations?
Rooftop co-working spaces offer inspiring city views and fresh air, enhancing the work environment and boosting creativity.
How do cultural influences impact rooftop designs worldwide?
Cultural influences shape rooftop designs by incorporating unique architectural styles and regional characteristics to reflect local heritage and traditions.
Conclusion
Rooftops have truly evolved from mere coverings to dynamic urban spaces that enhance sustainability and community engagement. The integration of green roofs, solar panels, and recreational areas reflects a commitment to eco-friendly living and social interaction.
Architects worldwide are pushing boundaries by incorporating cultural influences and innovative Curvspace designs that inspire you. These elements not only elevate the aesthetic appeal but also improve functionality and environmental performance.
As cities continue to grow, the potential of rooftops to contribute to urban life becomes increasingly significant. Embracing these trends can transform our skylines into vibrant, sustainable, and multifunctional spaces.
Show & Tell
We’d love to hear your thoughts about these ideas! Simply click the link to head over to your favorite platform and add your comments about this post there. We’d like to know about your insights, questions, or just saying hi.
More Curvspace Topic Pages
Disclosure
Our content is reader-supported. This means if you click on some of our links, then we may earn a commission. Commissions do not affect our editor’s opinions or evaluations. Learn more about our editorial process.

About the Editorial Staff
The Curvspace editorial team comprises a diverse group of experts on intermediate and threshold spaces in homes and workplaces. Architects and interior designers, civil engineers and artists, environmental and behavioral psychologists, sociologists and anthropologists. All collaborate to create helpful content, that explores the full potential of these often-overlooked areas to enhance our daily lives.